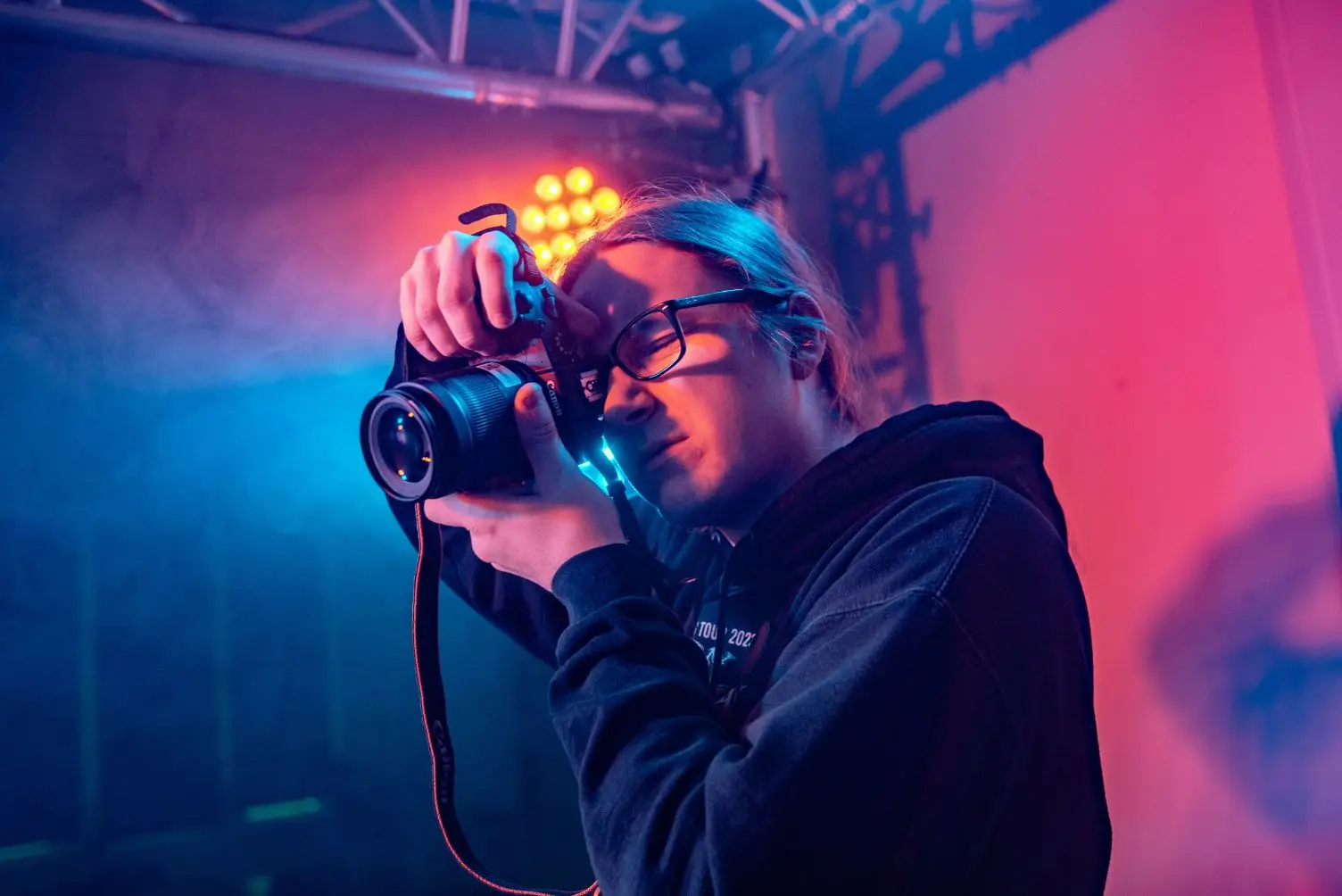
This article explores the concept of work experience, the various opportunities available, and practical steps you can take to secure work placements.
Gaining work experience whilst studying has become increasingly crucial for students looking to stand out in a competitive job market.
From traditional work placements to innovative T Level programmes, students today have more opportunities than ever to combine academic learning with real-world professional development. Understanding these options and how to access them can make the difference between graduating with just a qualification and graduating with both credentials and practical skills that employers seek.
What is work experience?

Work experience refers to any opportunity that allows you to observe, participate in, or contribute to a real workplace environment. It encompasses a broad range of activities, from short-term job shadowing to extended placements that run for several months or even a full academic year.
The primary purpose of work experience is to bridge the gap between theoretical learning and practical application. During these placements, students gain insights into daily operations within their chosen industry, develop professional skills, and build networks that can prove invaluable for future career development.
Work experience can take many forms, including unpaid placements, paid internships, part-time employment, voluntary work, and structured industry projects.
Work experience opportunities are available to students
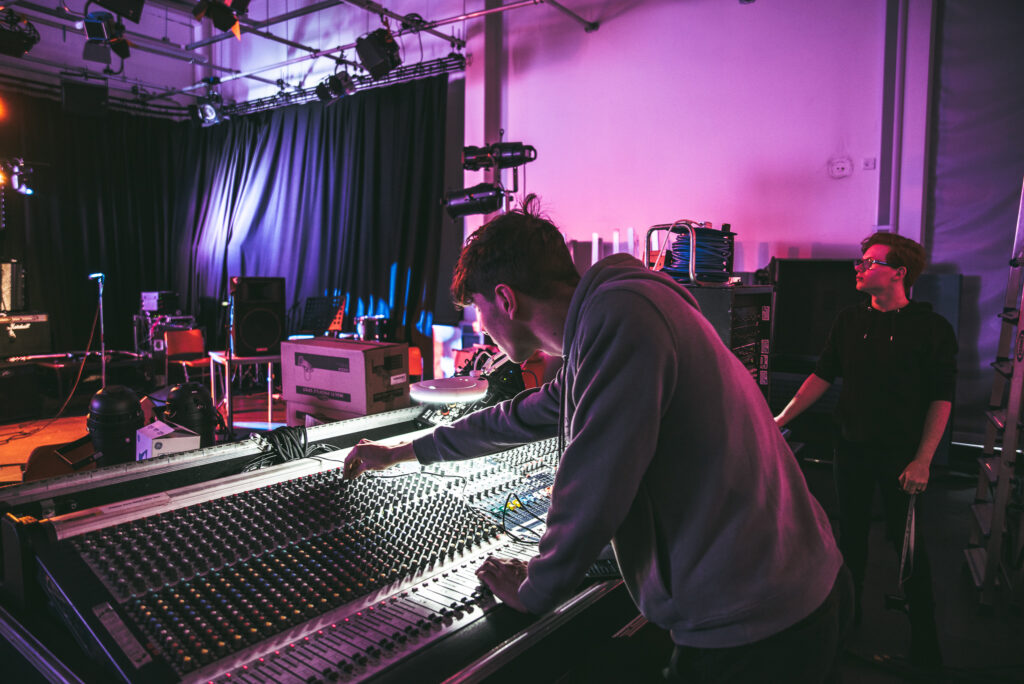

Traditional work placements
Many degree programmes incorporate mandatory work placements, often called industrial placements. These typically last between 6 and 12 months and are integrated into the degree structure, allowing students to gain substantial professional experience while maintaining their academic progression.
Summer internships
Summer internships provide concentrated work experience during academic breaks. These programmes, offered by companies across various sectors, typically last 8-12 weeks and often serve as recruitment pipelines for graduate positions. Many large corporations run structured internship programmes with formal application processes and competitive selection criteria.
Part-time employment
Balancing part-time work with studies allows students to earn money while gaining experience. Retail, hospitality, and customer service roles, whilst not always directly related to career aspirations, develop transferable skills such as communication, time management, and customer relations.
Voluntary work
Volunteering offers excellent opportunities to gain experience, particularly in sectors like charity, healthcare, education, and community services. Many organisations welcome student volunteers and provide structured programmes that develop both professional and personal skills.
Freelance and project-based work
The gig economy has created new opportunities for students to gain experience through freelance projects, particularly in creative industries, technology, and digital marketing. These arrangements offer flexibility that can accommodate academic schedules whilst building practical skills and professional portfolios.
How can I get work experience?

Research and identify opportunities
Start by researching companies and organisations within your field of interest. Visit their websites to look for formal work experience programmes, graduate schemes, or internship opportunities. Many employers post opportunities on their careers pages several months in advance, so early research is essential.
Leverage educational institutions
Your school, college, or university careers service is an invaluable resource. These departments often maintain relationships with local employers and can provide information about available opportunities, help with applications, and offer guidance on CV writing and interview preparation.
Network effectively
Networking remains one of the most effective ways to secure work experience. Attend industry events, join professional associations relevant to your field, and engage with professionals on platforms like LinkedIn. Don’t underestimate the power of informal conversations with family friends, teachers, or acquaintances who work in your area of interest.
Make speculative applications
Many work experience opportunities aren’t advertised publicly. Research companies you’d like to work with and send well-crafted speculative applications explaining your interest, what you hope to gain from the experience, and what you can contribute to their organisation.
Use online platforms
Websites like RateMyPlacement, Gradcracker, and AllAboutCareers list numerous work experience and internship opportunities across various sectors. Set up job alerts with relevant keywords to stay informed about new opportunities as they become available.
Where can I do work experience?
Private sector companies
From multinational corporations to small and medium enterprises, private companies across all sectors offer work experience opportunities. Technology firms, financial services, engineering companies, marketing agencies, and manufacturing businesses frequently host students for placements ranging from a few days to several months.
Public sector organisations
Government departments, local councils, the NHS, and educational institutions provide numerous work experience opportunities. These placements often offer insights into public service careers and can be particularly valuable for students interested in policy, healthcare, education, or public administration.
Non-profit organisations
Charities, social enterprises, and community organisations offer meaningful work experience opportunities, particularly for students interested in social impact careers. These placements often provide hands-on experience with project management, fundraising, community engagement, and programme delivery.
Creative and media industries
Television studios, radio stations, newspapers, advertising agencies, museums, galleries, and production companies regularly host students for work experience. These highly competitive placements require early applications and often benefit from networking and speculative approaches.
Healthcare and social care
Hospitals, GP practices, care homes, and community health organisations provide valuable experience for students considering healthcare careers. Some placements may require DBS checks or specific health screenings, so early application is essential.
Do you get paid for work experience?

The payment for work experience varies significantly depending on the type of placement, duration, and employer policies. Understanding your rights and what to expect helps you make informed decisions about which opportunities to pursue.
Unpaid placements
Many short-term work experience programmes, particularly those lasting less than two weeks, are unpaid. This is legal provided the placement is primarily for educational benefit rather than productive work. Employers should cover reasonable expenses such as travel costs and lunch allowances.
Paid internships
Longer placements, particularly those lasting more than a few weeks or involving productive work, should be paid at least the National Minimum Wage. The current rates vary by age, with specific provisions for apprentices and those under 18.
Academic credit vs. payment
Some work experience programmes offer academic credits instead of payment, particularly those integrated into degree programmes. These arrangements can be valuable as they contribute to your qualification whilst providing practical experience.
Expenses and benefits
Even unpaid placements should cover reasonable expenses. Some employers also provide additional benefits such as staff discounts, free meals, or travel allowances that can offset the lack of direct payment.
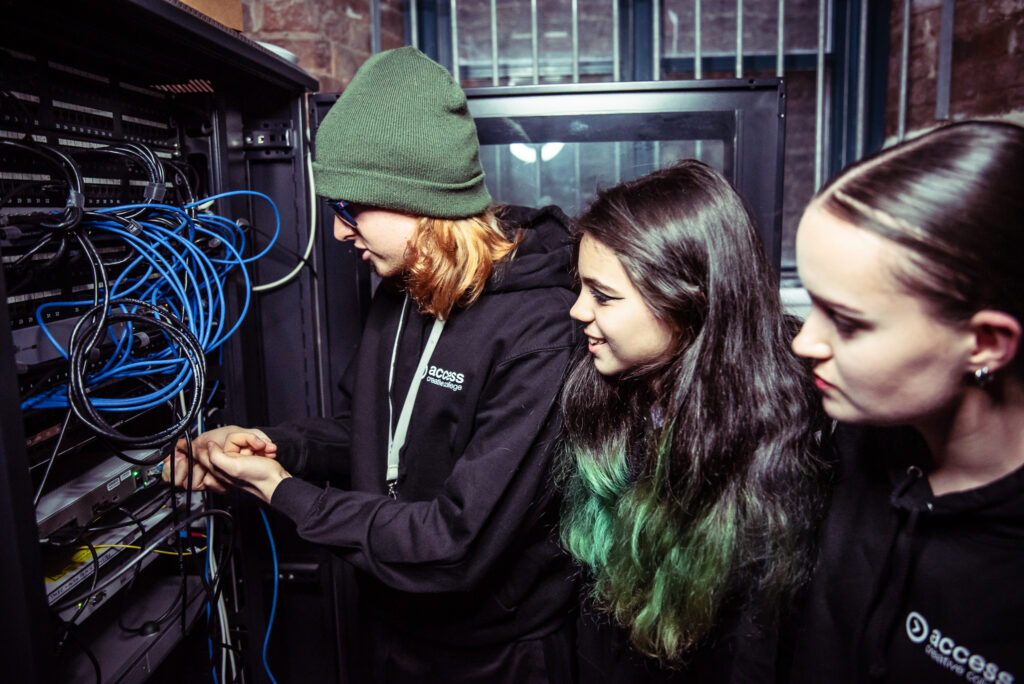
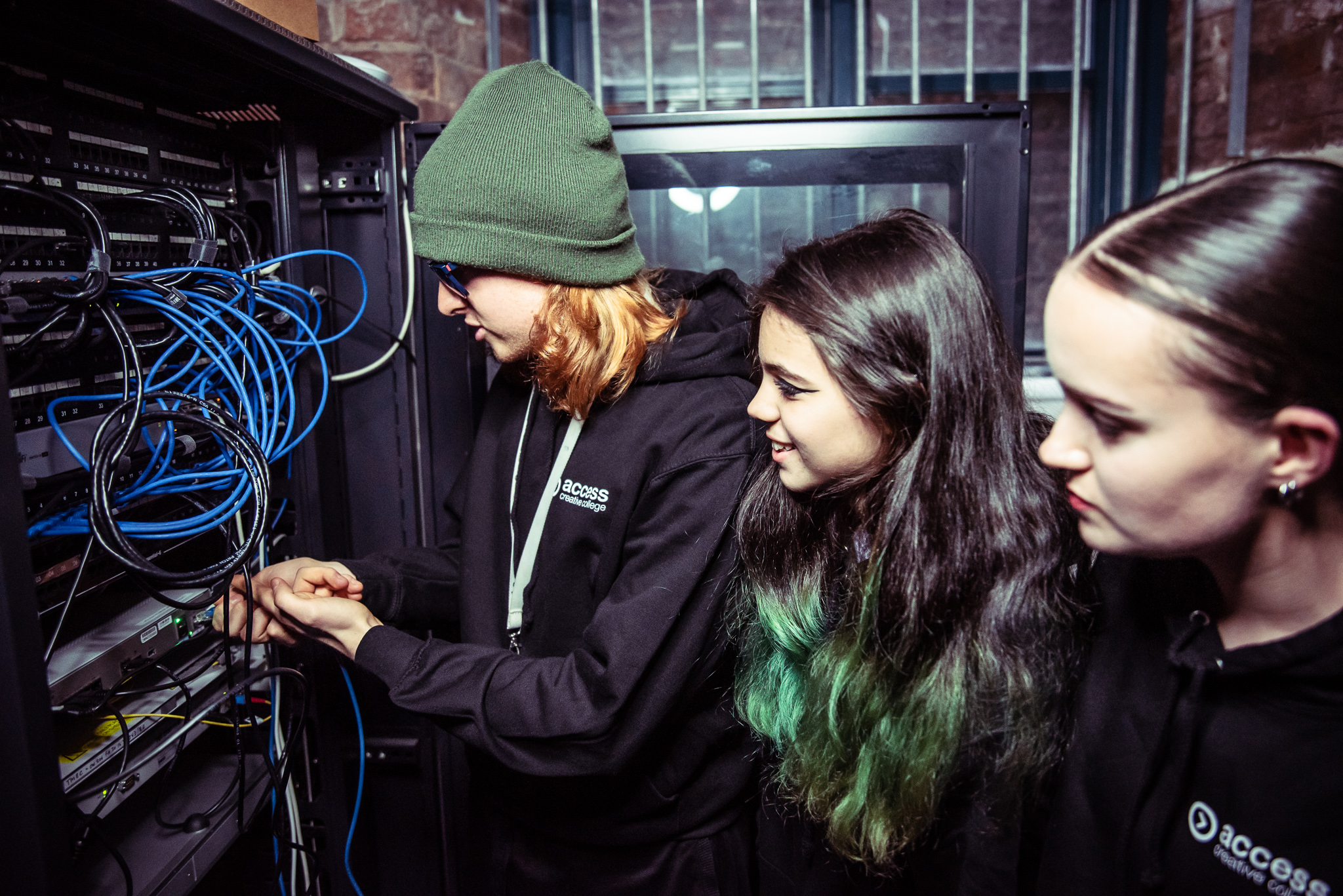
T Level work placement

T Levels represent a significant development in vocational education, combining academic study with substantial work placements. These qualifications, equivalent to three A Levels, include a mandatory industry placement lasting at least 315 hours (approximately 45 days).
Structure of T Level work placements
T Level work placements are integrated into the two-year programme, typically taking place during the second year of study. Students spend significant time in real workplace environments, applying theoretical knowledge gained in the classroom to practical situations.
Benefits of T Level work placements
These extended placements provide deep industry exposure, allowing students to develop both technical skills and professional behaviours. Employers often use T Level placements to identify and develop future employees, making them excellent pathways to employment or apprenticeships.
Industry coverage
T Level work placements span numerous sectors, including construction, digital technology, health and science, engineering and manufacturing, and creative and design industries. This breadth ensures opportunities across various career paths.
Access Creative College offers T Level courses as part of its curriculum, with places still available for this September for:
What can I do for work experience?

Shadow professionals
Job shadowing allows you to observe professionals in their daily work, providing insights into career paths and workplace cultures. These brief placements, typically lasting one to five days, are often easier to arrange and can inform longer-term career decisions.
Participate in project work
Many organisations offer students opportunities to contribute to specific projects, providing hands-on experience whilst delivering value to the employer. These might include research projects, marketing campaigns, or community initiatives.
Assist with events
Event management provides excellent transferable skills and networking opportunities. Many event organisations welcome student volunteers for conferences, exhibitions, fundraising events, or community activities.
Content creation and digital marketing
Students with digital skills can contribute to organisations’ online presence through social media management, blog writing, website development, or video production. These opportunities are particularly relevant given the growing importance of digital marketing.
Research and analysis
Students can contribute to market research, policy analysis, or academic research projects. These opportunities develop analytical skills whilst providing valuable support to organisations.
Which college courses offer work experience?

Vocational and technical courses
Courses in healthcare, engineering, construction, hospitality, and creative industries typically include substantial work experience components. These programmes are designed to prepare students for direct entry into employment or further professional development.
Business and management studies
Many business courses include placement years or shorter work experience modules. These might involve working in various business functions such as marketing, human resources, finance, or operations management.
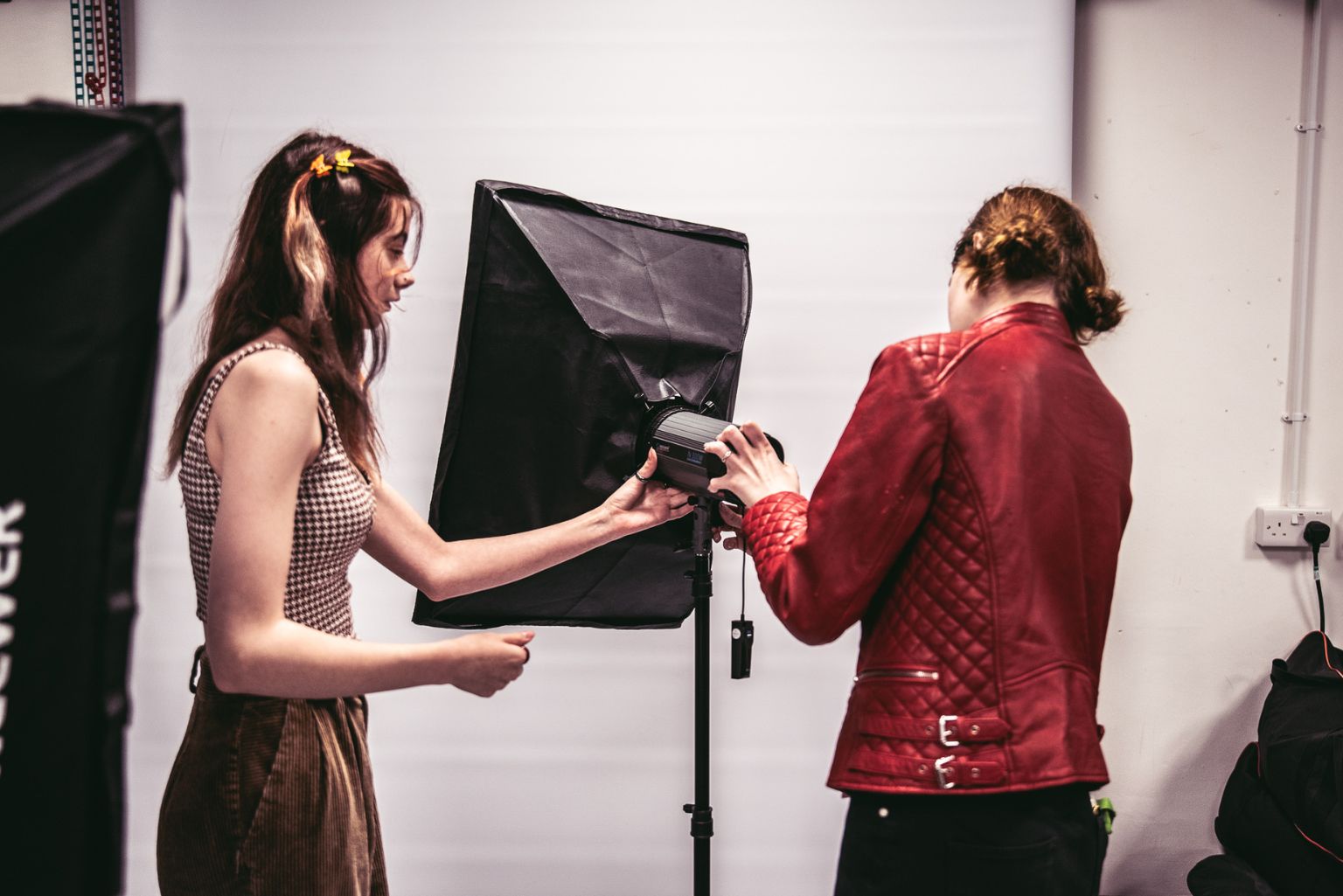
Creative arts and media
Art, design, media production, and creative courses often incorporate real-world projects and industry placements. Students might work with galleries, production companies, design agencies, or media organisations.
Science and technology
STEM courses increasingly include industrial placements, allowing students to apply theoretical knowledge in research and development environments, engineering firms, or technology companies.
Access Creative College: your gateway to creative and technical careers

At Access Creative College we believe we’re an exceptional choice for students seeking courses that combine academic excellence with substantial work experience opportunities. Specialising in creative and digital industries, the college offers programmes that are specifically designed to prepare students for successful careers in rapidly evolving creative sectors.
Our courses are in areas such as Music Production, Games Development, Film and TV Production, and Digital Design, and are developed in close partnership with industry professionals. This collaboration ensures that curriculum content remains current with industry standards whilst providing students with direct access to professional networks and work experience opportunities.
What sets us apart is our commitment to employability. Our career services team works closely with students to identify suitable work experience opportunities, provide application support, and facilitate connections with potential employers.
Building your professional future starts today
Gaining work experience whilst studying has evolved from a helpful addition to an essential component of career preparation.
Whether through traditional work placements, innovative T Level programmes, or creative industry collaborations, numerous pathways exist to build professional credentials during your studies.
Apply online for a T Level course today!